Generative AI-driven Chatbots versus Workflow Agents
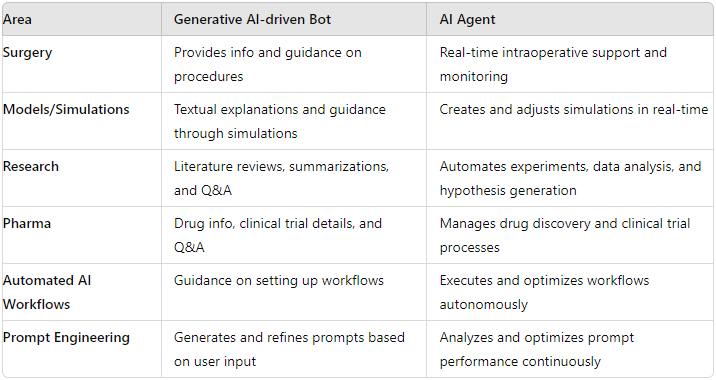
Surgery
Generative AI-driven Chatbot
Function: Provides conversational assistance, answering questions about surgical procedures, guidelines, and protocols.
Usage: Assisting surgeons and medical staff with information retrieval during preoperative planning or postoperative care.
Example: A bot that answers queries about surgical steps, risks, and best practices based on extensive medical texts.
Generative AI-driven Agent
Function: Acts autonomously to support complex surgical tasks, such as real-time intraoperative guidance, monitoring, and decision support.
Usage: Assisting during surgery with real-time data analysis, identifying critical moments, and suggesting actions.
Example: An AI agent that integrates with surgical tools to provide real-time feedback, monitor vital signs, and alert surgeons to potential complications.
Models/Simulations
Generative AI-driven Chatbot
Function: Generates textual descriptions and explanations of models and simulations, guiding users through scenarios.
Usage: Providing textual support and explanations in virtual training environments.
Example: A bot that explains each step of a surgical simulation and answers trainee questions about the procedure.
Function: Creates and controls simulations, adjusting parameters in real-time to create realistic training scenarios.
Usage: Managing and dynamically adjusting simulations based on trainee performance or new data inputs.
Example: An AI agent that runs a surgical simulation, adapting the scenario in real-time based on the trainee's actions to create varied and realistic training experiences.
Research
Generative AI-driven Chatbot
Function: Assists researchers by generating literature reviews, summarizing papers, and answering questions about specific research topics.
Usage: Supporting researchers with information retrieval and synthesis.
Example: A bot that provides summaries of the latest research articles and answers questions about methodologies and findings.
Generative AI-driven Agent
Function: Conducts research autonomously, from hypothesis generation to data analysis, and can manage experimental workflows.
Usage: Automating parts of the research process, such as running simulations, analyzing large datasets, and optimizing experiments.
Example: An AI agent that designs experiments, runs simulations, collects and analyzes data, and proposes new hypotheses based on findings.
Pharma
Generative AI-driven Chatbot
Function: Provides information about drugs, clinical trials, and pharmaceutical research through conversational interactions.
Usage: Assisting healthcare professionals and patients with drug information and clinical trial details.
Example: A bot that answers questions about drug interactions, side effects, and ongoing clinical trials.
Function: Manages and optimizes drug discovery processes, from virtual screening to clinical trial management.
Usage: Enhancing drug development by autonomously conducting virtual experiments, optimizing compound structures, and managing trial logistics.
Example: An AI agent that autonomously screens millions of compounds, predicts their efficacy, and designs optimal clinical trial protocols.
Automated AI Workflows
Generative AI-driven Chatbot
Function: Provides guidance and documentation for setting up and using automated AI workflows.
Usage: Assisting users with setting up and troubleshooting automated workflows.
Example: A bot that answers questions about configuring AI workflow tools and provides step-by-step setup guides.
Generative AI-driven Agent
Function: Executes and manages automated workflows, making real-time decisions to optimize processes.
Usage: Running complex workflows autonomously, making adjustments based on data inputs and performance metrics.
Example: An AI agent that orchestrates a series of automated data processing tasks, optimizes resource allocation, and resolves issues without human intervention.
Prompt Engineering
Generative AI-driven Chatbot
Function: Generates optimized prompts for various AI models based on user inputs.
Usage: Helping users create effective prompts for AI tasks.
Example: A bot that suggests and refines prompts for language models to achieve desired outputs in different contexts.
Function: Analyzes prompt performance, iteratively tests and refines prompts, and adapts to changing requirements.
Usage: Continuously improving prompt effectiveness through autonomous testing and optimization.
Example: An AI agent that monitors the performance of prompts in real-time, identifies areas for improvement, and autonomously adjusts them to enhance output quality.